Données techniques
| Formule | C27H20ClFN4O4 |
||||||
| Poids moléculaire | 518.92 | Numéro CAS | 1028486-01-2 | ||||
| Solubilité (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 100 mg/mL (192.7 mM) | ||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Ajouter les solvants au produit individuellement et dans lordre.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml signifie légèrement soluble ou insoluble. * Veuillez noter que Selleck teste la solubilité de tous les composés en interne, et la solubilité réelle peut différer légèrement des valeurs publiées. Ceci est normal et est dû à de légères variations dun lot à lautre. * Expédition à température ambiante (les tests de stabilité montrent que ce produit peut être expédié sans aucune mesure de refroidissement.) |
|||||||
Préparation des solutions mères
Activité biologique
| Description | L'Alisertib (MLN8237) est un inhibiteur sélectif de l'Aurora A avec une IC50 de 1,2 nM dans un essai acellulaire, et il présente une sélectivité >200 fois supérieure pour Aurora A que pour Aurora B. Ce composé induit un arrêt du cycle cellulaire, l'apoptose et l'autophagie. Phase 3. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cibles |
|
||
| In vitro | L'Alisertib (MLN8237) présente une sélectivité >200 fois supérieure pour Aurora A que pour l'Aurora B structurellement apparentée, avec une IC50 de 396,5 nM, et n'a pas d'activité significative contre 205 autres kinases. Le traitement avec ce composé (0,5 μM) inhibe la phosphorylation d'Aurora A dans les cellules MM1.S et OPM1, sans affecter la phosphorylation de l'histone H3 médiée par Aurora B. Il inhibe significativement la prolifération cellulaire dans les lignées cellulaires de myélome multiple (MM) avec des valeurs d'IC50 de 0,003-1,71 μM, et présente une activité anti-prolifération plus puissante contre les cellules MM primaires et les lignées cellulaires MM en présence de cellules stromales de la moelle osseuse, ainsi que d'IL-6 et d'IGF-1 que contre les cellules MM seules. À 0,5 μM, il induit une augmentation de 2 à 6 fois de la phase G2/M dans les cellules MM primaires et les lignées cellulaires, ainsi qu'une apoptose et une sénescence significatives, impliquant la régulation positive de p53, p21 et p27, ainsi que le clivage de PARP, caspase 3 et caspase 9. De plus, il montre un fort effet anti-MM synergique avec l'hexadécadrol, ainsi qu'un effet additif avec la doxorubicine et le LDP-341. Ce composé (0,5 μM) provoque l'inhibition de la formation de colonies des lignées cellulaires d'adénocarcinome œsophagien FLO-1, OE19 et OE33, et induit une augmentation significative du pourcentage de cellules polyploïdes, puis une augmentation du pourcentage de cellules en phase sub-G1, qui peut être davantage améliorée en combinaison avec le NSC 119875 (2,5 μM), impliquant une induction plus élevée de TAp73β, PUMA, NOXA, la caspase-3 clivée et le PARP clivé par rapport à un traitement à agent unique. |
||
| In vivo | L'Alisertib (MLN8237) réduit significativement la charge tumorale avec une inhibition de la croissance tumorale (TGI) de 42% et 80% à 15 mg/kg et 30 mg/kg, respectivement, et prolonge la survie des souris par rapport au contrôle. |
||
| Caractéristiques | Premier inhibiteur oralement disponible de l'Aurora A. |
Protocole (de référence)
| Test kinase : |
|
|---|---|
| Test cellulaire : |
|
| Étude animale : |
|
Références
|
Validation du produit par le client
-S113303W0120130926.gif)
-
Données de [ Oncogene , 2014 , 33, 3550-60 ]
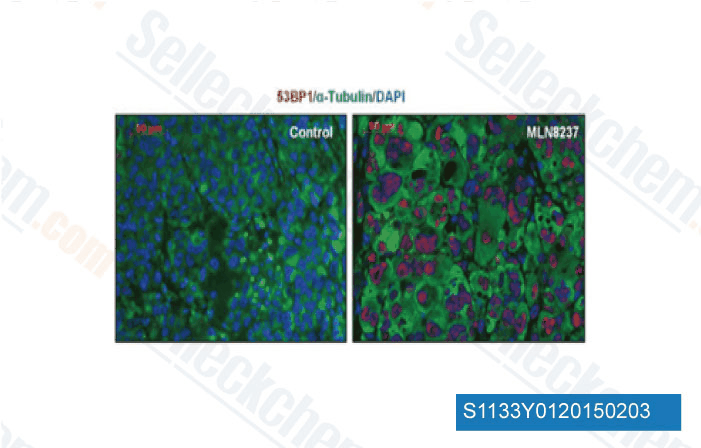
-
Données de [ EMBO Mol Med , 2013 , 5(1), 149-66 ]
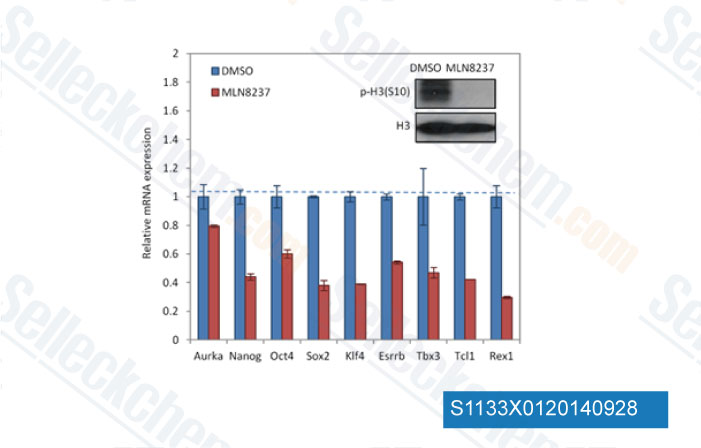
-
Données de [ Cell Stem Cell , 2012 , 11, 179-94 ]
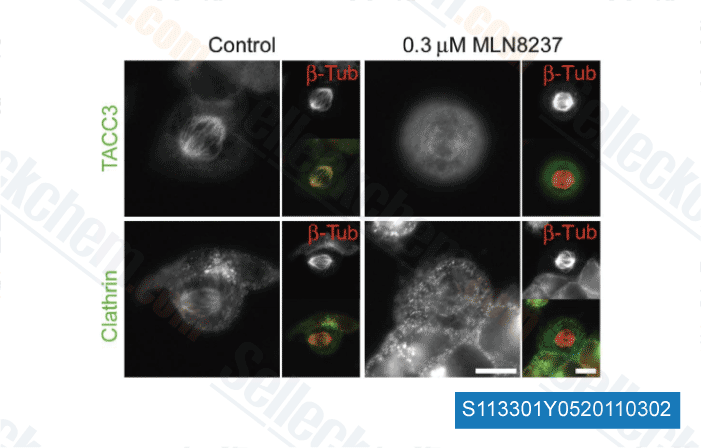
-
Données de [ EMBO J , 2012 , 30, 906-19 ]
Sellecks Alisertib (MLN8237) A été cité par 380 Publications
| Centromere protection requires strict mitotic inactivation of the Bloom syndrome helicase complex [ Nat Commun, 2025, 16(1):7832] | PubMed: 40846865 |
| Aurora A regulates the material property of spindle poles to orchestrate nuclear organization at mitotic exit [ EMBO J, 2025, 10.1038/s44318-025-00564-4] | PubMed: 40940421 |
| Targeted inhibition of Aurora kinase A promotes immune checkpoint inhibition efficacy in human papillomavirus-driven cancers [ J Immunother Cancer, 2025, 13(1)e009316] | PubMed: 39773561 |
| An Aurora kinase A-BOD1L1-PP2A B56 axis promotes chromosome segregation fidelity [ Cell Rep, 2025, 44(2):115317] | PubMed: 39970043 |
| The AURKA inhibitor alters the immune microenvironment and enhances targeting B7-H3 immunotherapy in glioblastoma [ JCI Insight, 2025, e173700] | PubMed: 39928563 |
| CDK1-mediated phosphorylation of LDHA fuels mitosis through LDHB-dependent lactate oxidation [ EMBO Rep, 2025, 10.1038/s44319-025-00573-8] | PubMed: 40940446 |
| Cellular senescence as a prognostic marker for predicting breast cancer progression in 2D and 3D organoid models [ Biomed Pharmacother, 2025, 189:118324] | PubMed: 40616881 |
| Actionable heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma therapy-induced senescence [ Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2025, 74(7):207] | PubMed: 40374812 |
| Aurora B maintains spherical shape of mitotic cells via simultaneously stabilizing myosin II and vimentin [ J Mol Cell Biol, 2025, mjaf023] | PubMed: 40795355 |
| O 6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) expression in U1242 glioblastoma cells enhances in vitro clonogenicity, tumor implantation in vivo, and sensitivity to alisertib-carboplatin combination treatment [ Front Cell Neurosci, 2025, 19:1552015] | PubMed: 40336841 |
POLITIQUE DE RETOUR
La politique de retour inconditionnelle de Selleck Chemical garantit une expérience dachat en ligne fluide à nos clients. Si vous nêtes en aucun cas satisfait de votre achat, vous pouvez retourner tout article dans les 7 jours suivant sa réception. En cas de problèmes de qualité du produit, quil sagisse de problèmes liés au protocole ou au produit, vous pouvez retourner tout article dans les 365 jours suivant la date dachat initiale. Veuillez suivre les instructions ci-dessous lors du retour des produits.
EXPÉDITION ET STOCKAGE
Les produits Selleck sont transportés à température ambiante. Si vous recevez le produit à température ambiante, soyez assuré que le service dinspection de la qualité de Selleck a mené des expériences pour vérifier que le placement à température normale pendant un mois naffectera pas lactivité biologique des produits en poudre. Après réception, veuillez stocker le produit conformément aux exigences décrites dans la fiche technique. La plupart des produits Selleck sont stables dans les conditions recommandées.
NON DESTINÉ À UN USAGE HUMAIN, VÉTÉRINAIRE DIAGNOSTIQUE OU THÉRAPEUTIQUE.
