Données techniques
| Formule | C16H15ClN4O2 |
||||||
| Poids moléculaire | 330.77 | Numéro CAS | 263707-16-0 | ||||
| Solubilité (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 66 mg/mL (199.53 mM) | ||||
| Ethanol | 5 mg/mL (15.11 mM) | ||||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Ajouter les solvants au produit individuellement et dans lordre.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml signifie légèrement soluble ou insoluble. * Veuillez noter que Selleck teste la solubilité de tous les composés en interne, et la solubilité réelle peut différer légèrement des valeurs publiées. Ceci est normal et est dû à de légères variations dun lot à lautre. * Expédition à température ambiante (les tests de stabilité montrent que ce produit peut être expédié sans aucune mesure de refroidissement.) |
|||||||
Préparation des solutions mères
Activité biologique
| Description | ESI-09 est un inhibiteur spécifique de la protéine d'échange directement activée par le cAMP (EPAC) avec une IC50 de 3,2 μM et 1,4 μM pour EPAC1 et EPAC2, respectivement, >100 fois plus sélectif que la PKA. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cibles |
|
||||
| In vitro | ESI-09, un nouvel antagoniste non nucléotidique cyclique de l'EPAC, capable de bloquer spécifiquement l'activation intracellulaire de Rap1 médiée par l'EPAC et la phosphorylation d'Akt, ainsi que la sécrétion d'insuline médiée par l'EPAC dans les cellules β pancréatiques. D'autre part, ce composé ne parvient pas à supprimer la phosphorylation d'Akt induite par le facteur de croissance épidermique (EGF) dans les cellules AsPC1. Dans les cellules cancéreuses pancréatiques, cet antagoniste inhibe la migration et l'invasion cellulaires en diminuant l'adhésion cellulaire induite par 007-AM de manière dose-dépendante. Ce produit chimique réduit significativement le nombre de bactéries intracellulaires et totales dans les cellules endothéliales de la veine ombilicale humaine. Il antagonise efficacement la différenciation des cellules de Schwann (SC) induite par le CPT-cAMP ainsi que la formation de myéline. Dans les cultures de SC-neurones, ce composé réduit considérablement le nombre de SCs positives pour O1 et MBP sans compromettre la santé des neurones ou des SCs elles-mêmes. | ||||
| In vivo | ESI-09 (10 mg/kg/jour, i.p.), par inhibition pharmacologique de l'EPAC1, protège les souris WT C57BL/6 de la rickettsiose SFG fatale. |
Protocole (de référence)
| Étude animale :[2] |
|
|---|
Références
|
Validation du produit par le client
-
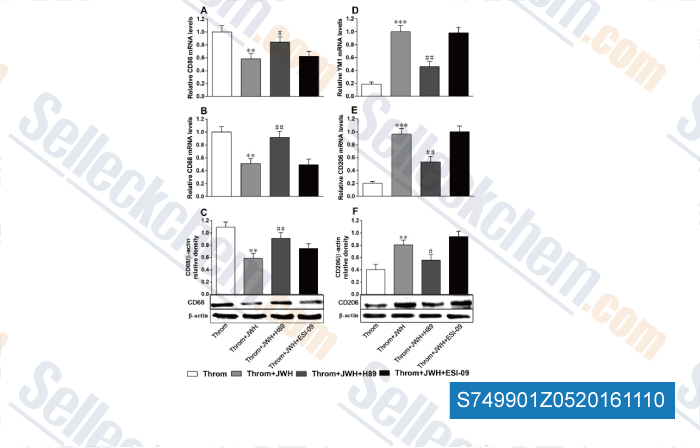
, , Brain Behav Immun, 2016, 58:118-129.
-
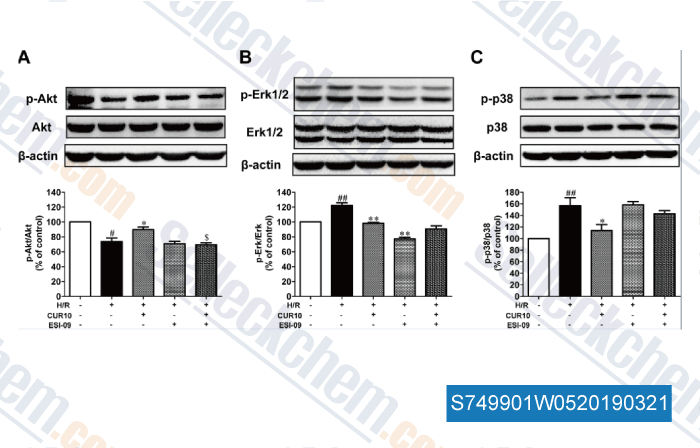
Données de [ , , Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109:1268-1275 ]
-
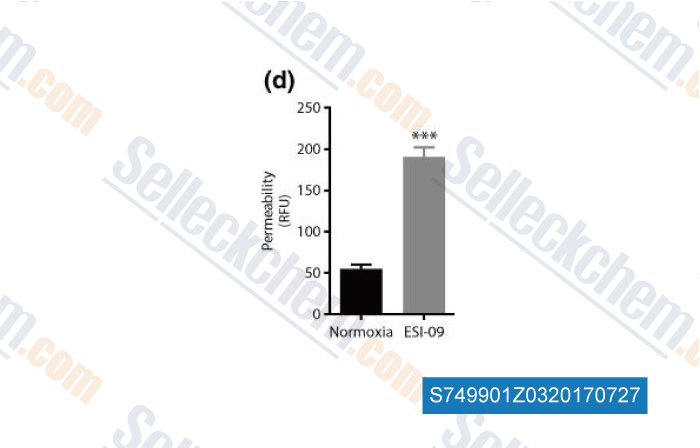
Données de [ , , Acta Diabetol, 2017, 54(6):581-591 ]
-
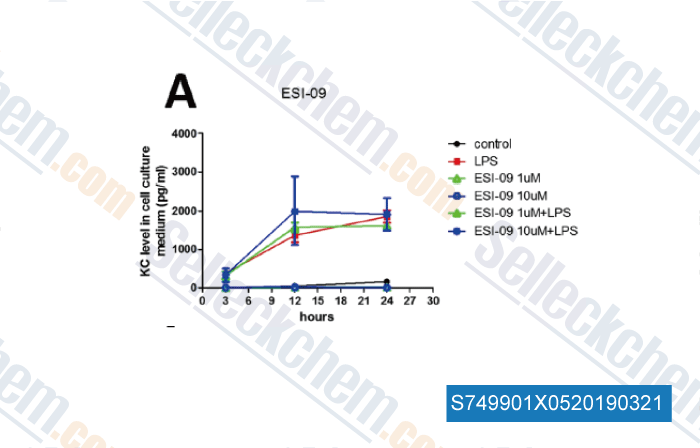
Données de [ , , Inflammation, 2018, 41(3):1093-1103 ]
Sellecks ESI-09 A été cité par 14 Publications
| Ginsenoside Ro prevents endothelial injury via promoting Epac1/AMPK- mediated mitochondria protection in early diabetic retinopathy [ Pharmacol Res, 2025, 211:107562] | PubMed: 39732351 |
| Inhibition of exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP as a strategy for broad-spectrum antiviral development [ J Biol Chem, 2023, 299(6):104749] | PubMed: 37100284 |
| PNX14 but not PNX20 as a novel regulator of preadipocyte differentiation via activating Epac-ERK signaling pathway in Gallus gallus [ Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2023, 335:114232] | PubMed: 36774983 |
| Vitexin Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Regulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Epac1-Rap1 Signaling [ Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021:9921982] | PubMed: 34257823 |
| Terbutaline attenuates LPS-induced injury of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by cAMP/Epac signaling [ Drug Dev Res, 2021, 10.1002/ddr.21901] | PubMed: 34846077 |
| Knockdown of GPSM1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Promotes the Apoptosis of B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells by Suppressing the ADCY6-RAPGEF3-JNK Signaling Pathway [ Pathol Oncol Res, 2021, 27:643376] | PubMed: 34257610 |
| Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac) 1 plays an essential role in stress-induced exercise capacity by regulating PGC-1α and fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle. [ Pflugers Arch, 2020, 472(2):195-216] | PubMed: 31955265 |
| Curcumin pretreatment protects against hypoxia/reoxgenation injury via improvement of mitochondrial function, destabilization of HIF-1α and activation of Epac1-Akt pathway in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [Wang X, et al. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109:1268-1275] | PubMed: 30551377 |
| Protective Effect of Quercetin in LPS-Induced Murine Acute Lung Injury Mediated by cAMP-Epac Pathway [Wang XF, et al. Inflammation, 2018, 41(3):1093-1103] | PubMed: 29569077 |
| Activation of Epac alleviates inflammation and vascular leakage in LPS-induced acute murine lung injury [Wang X, et al. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 96:1127-1136] | PubMed: 29174852 |
POLITIQUE DE RETOUR
La politique de retour inconditionnelle de Selleck Chemical garantit une expérience dachat en ligne fluide à nos clients. Si vous nêtes en aucun cas satisfait de votre achat, vous pouvez retourner tout article dans les 7 jours suivant sa réception. En cas de problèmes de qualité du produit, quil sagisse de problèmes liés au protocole ou au produit, vous pouvez retourner tout article dans les 365 jours suivant la date dachat initiale. Veuillez suivre les instructions ci-dessous lors du retour des produits.
EXPÉDITION ET STOCKAGE
Les produits Selleck sont transportés à température ambiante. Si vous recevez le produit à température ambiante, soyez assuré que le service dinspection de la qualité de Selleck a mené des expériences pour vérifier que le placement à température normale pendant un mois naffectera pas lactivité biologique des produits en poudre. Après réception, veuillez stocker le produit conformément aux exigences décrites dans la fiche technique. La plupart des produits Selleck sont stables dans les conditions recommandées.
NON DESTINÉ À UN USAGE HUMAIN, VÉTÉRINAIRE DIAGNOSTIQUE OU THÉRAPEUTIQUE.
