Usage réservé à la recherche
Phospho-Chk1 (Ser296) Antibody [F19D13]
N° de cat.: F5055
Application:
Réactivité:
Informations dutilisation
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB |
| Réactivité |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Tampon de stockage |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Stockage (à partir de la date de réception) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
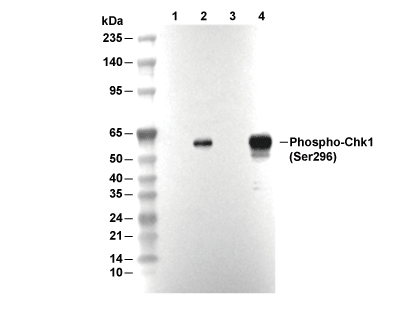
| Poids moléculaire prédit Poids moléculaire observé |
|---|
| 56 kDa 56 kDa |
| *Pourquoi les poids moléculaires prédit et réel diffèrent-ils? Les raisons suivantes peuvent expliquer les différences entre le poids moléculaire prédit et réel des protéines. |
| Contrôle positif | HeLa cells (UV, 100 mJ/cm2, 2 h); NIH/3T3 cells (UV, 100 mJ/cm2, 2 h); C6 cells (UV, 100 mJ/cm2, 2 h); HT-29 cells (serum starved; UV, 100mJ/cm2, 1 h) |
|---|---|
| Contrôle négatif | HeLa cells; NIH/3T3 cells; C6 cells |
Méthodes expérimentales
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution ( recommending 5% BSA solution)
for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Description biologique
| Spécificité |
|---|
| Phospho-Chk1 (Ser296) Antibody [F19D13] detects endogenous levels of total Chk1 protein only when it is phosphorylated at Ser296. |
| Localisation subcellulaire |
|---|
| Chromosome, Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton, Nucleus |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| O14757 |
| Clone |
|---|
| F19D13 |
| Synonyme |
|---|
| Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1; CHK1 checkpoint homolog; Cell cycle checkpoint kinase; Checkpoint kinase-1; CHEK1; CHK1 |
| Contexte |
|---|
| Phospho-Chk1 (Ser296) represents the activated form of Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1), a serine/threonine kinase crucial for the DNA damage response (DDR) that integrates ATR/ATM signaling to enforce cell cycle checkpoints, stabilize replication forks, and promote DNA repair or apoptosis. Chk1 is a protein with an N-terminal kinase domain containing the conserved catalytic triad (Lys38, Glu91, Asp147 in the activation loop) and a regulatory C-terminal tail with SQ sites (Ser317, Ser345) for ATR phosphorylation, plus an autophosphorylation site at Ser296 located in an unstructured loop. Phosphorylation at Ser296 occurs via an ATR-dependent cis-intramolecular autophosphorylation mechanism only after priming phosphorylation at Ser317/Ser345, events that relieve autoinhibition, stabilize the active kinase conformation, and expose Ser296 for autophosphorylation. Phospho-Ser296 Chk1 enhances checkpoint proficiency by increasing kinase activity toward Cdc25 phosphatases (Cdc25A Ser76 for β-TrCP-mediated proteolysis, Cdc25B/C Ser216/287 for 14-3-3 sequestration), thereby preventing premature CDK1/2 activation and promoting S/G2/M cell cycle arrest. It also phosphorylates additional effectors such as Treslin, Claspin, and FanD2 to coordinate replication fork restart, homologous recombination, and translesion synthesis, while centrosomal phospho-Chk1 inhibits Cdc25B-CDK1 to block mitotic entry until DNA damage is resolved. This multi-site activation cascade ensures robust DDR signaling, and Ser296A mutants display defective checkpoint arrest and synthetic lethality with ATR inhibitors. Phospho-Chk1(Ser296) marks replication stress and predicts sensitivity to Chk1 inhibitors, which abrogate fork protection and induce mitotic catastrophe in p53-deficient tumors, while Chk1 overexpression correlates with chemoresistance in ovarian, lung, and hematologic malignancies. |
| Références |
|---|
|
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.