Wnt proteins form a family of highly conserved secreted signaling molecules that regulate cell-to-cell interactions during embryogenesis. Wnt signalling pathway plays a key role in the development of CSC(Cancer stem cell) and it may be a significant step in the development of a large number of tomours. As currently understood, Wnt proteins bind to receptors of the Frizzled and LRP families on the cell surface. [show the full text]
Wnt/beta-catenin inhibiteurs/activateurs (Wnt/beta-catenin Inhibitors/Activators)
Autre Stem Cells & Wnt Inhibiteurs
- Inhibiteurs en vedette
- Inhibiteurs (34)
- Modulateurs (3)
- Agonistes (4)
- Activateurs (11)
- Agonistes (4)
| N° Cat. | Nom du produit | Information | Citations dutilisation du produit | Validations de produits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S7086 | IWR-1-endo | IWR-1-endo (endo-IWR 1, IWR-1) est un inhibiteur de la voie Wnt avec une IC50 de 180 nM dans les cellules L exprimant Wnt3A, il induit les niveaux de protéine Axin2 et favorise la phosphorylation de la β-caténine en stabilisant les complexes de destruction échafaudés par l'Axin. |
|
|
| S8968 | PRI-724 (Foscenvivint) | Foscenvivint (PRI-724) est un inhibiteur puissant et spécifique qui perturbe l'interaction de la β-caténine et de la CBP. |
|
|
| S7085 | IWP-2 | IWP-2 est un inhibiteur du traitement et de la sécrétion de Wnt avec un IC50 de 27 nM dans un essai sans cellules, un blocage sélectif de la palmitoylation de Wnt médiée par Porcn, n'affecte pas Wnt/β-caténine en général et n'affiche aucun effet contre les réponses cellulaires stimulées par Wnt. IWP-2 inhibe spécifiquement la CK1δ. |
|
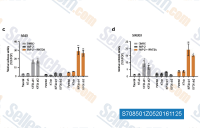
|
| S0733 | Tegatrabetan (BC-2059) | Tegatrabetan (BC-2059, Tegavivint), un antagoniste de la β-caténine, perturbe la liaison de la β-caténine avec la protéine d'échafaudage transducine β-like 1 (TBL1) et la dégradation protéasomale, entraînant une diminution des niveaux nucléaires de β-caténine. |
|
|
| S3842 | Isoquercitrin | L'Isoquercitrin (Hirsutrin, 3-Glucosylquercetin, Quercetin 3-o-glucopyranoside), un composé flavonoïde à activité anticancéreuse isolé de Bidens bipinnata L, est un inhibiteur de Wnt/ A-caténine qui agit en aval de la translocation nucléaire de la A-caténine. |
|
|
| S2662 | ICG-001 | ICG-001 antagonise la transcription médiatisée par Wnt/β-caténine/TCF et se lie spécifiquement à la protéine de liaison à CREB (CBP) avec un IC50 de 3 μM, mais n'est pas le coactivateur transcriptionnel p300 apparenté. ICG-001 induit l'apoptose. |
|
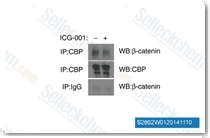
|
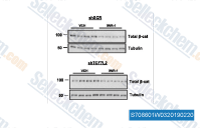
| S1263 | CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021, CT99021) est un inhibiteur de GSK-3α et GSK-3β avec des valeurs d'IC50 de 10 nM et 6,7 nM, respectivement. Il ne présente pas de réactivité croisée contre les kinases dépendantes des cyclines (CDK) et montre une sélectivité 350 fois supérieure envers GSK-3β par rapport aux CDK. Ce composé fonctionne comme un activateur de Wnt/β-catenin et induit l'autophagy. |
|
|
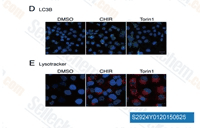
| S2924 | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) Hydrochloride | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021; CT99021) HCl est le chlorhydrate de CHIR-99021, un inhibiteur de GSK-3α/β avec une IC50 de 10 nM/6,7 nM; CHIR-99021 montre une sélectivité supérieure à 500 fois pour GSK-3 par rapport à ses homologues les plus proches Cdc2 et ERK2. CHIR-99021 est un puissant activateur pharmacologique de la voie de signalisation Wnt/beta-catenin. CHIR-99021 sauve significativement l'autophagy induite par la lumière et augmente les protéines GR, RORα et celles liées à l'autophagie. |
|
|
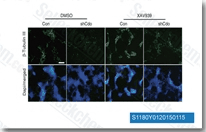
| S1180 | XAV-939 | XAV-939 (NVP-XAV939) inhibe sélectivement la transcription médiée par Wnt/β-caténine via l'inhibition de la tankyrase1/2 avec une IC50 de 11 nM/4 nM dans les essais sans cellules, régule les niveaux d'axine et n'affecte pas CRE, NF-κB ou TGF-β. |
|
|
| S5992 | Heparan Sulfate | Heparan sulfate (HS, Heparitin sulfate, Alpha-idosane, HHS 5, N-Acetylheparan Sulfate, Suleparoid, Tavidan), un constituant des protéoglycanes HS (HSPGs), est un polysaccharide linéaire présent à la surface cellulaire. Heparan sulfate influence l'affinité de liaison des cellules épithéliales intestinales (IEC) au Wnt, favorisant ainsi l'activation de la signalisation canonique du Wnt et facilitant la régénération des cryptes de l'intestin grêle après une lésion épithéliale. |
|
|
The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is an important mechanism of study for researchers of human diseases as it plays a role in oncology when overactivated, however, reduced signalling of this pathway also results in abnormal bone development and neurodegenerative illnesses. Depending on the indication of use, development of inhibitors or activators of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is an important area of focus.
Normally, regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway occurs by a large protein assembly called the β-catenin destruction complex that maintains low concentrations of β-catenin in the cytoplasm, and consequently in the nucleus. The β-catenin destruction complex is comprised of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3α/ GSK3β), casein kinase Iα (CKIα), Axin1/Axin2 scaffolding, and adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) – a tumor suppressor protein. Recruitment of β-catenin to the destruction complex leads to the phosphorylation of β-catenin N-terminus residues by CKIα and GSK3, following which ubiquitination and degradation events occur. Sequestering β-catenin at several N-terminal serine and threonine residues to the β-catenin destruction complex are Axin and APC. Similarly, it is believed these constituents of the β-catenin destruction complex regulate β-catenin efflux from the nucleus. The low concentration of β-catenin in the cell restricts β-catenin to the essential role of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. An additional mechanism controlling the expression of Wnt signalling in the cell involves the inhibition of Wnt specific gene transcription by the T-cell factor (TCF) family of proteins.[1]
Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is signified by the formation of a “Wnt signalosome” – a large protein complex that develops following the recognition of Wnt protein on the cell surface by a set of proteins called the seven-pass transmembrane Frizzled (Fz) family and its co-receptor, low density lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP5/LRP6).ii The Wnt signalosome inhibits the activity of the β-catenin destruction complex by recruiting several components of the destruction complex to the membrane. As a consequence, the buildup of β-catenin’s unphosphorylated form results in the cytoplasm and subsequently in the nucleus. It is in the nucleus where rising concentrations of β-catenin combine with TCF proteins to transform this protein from an inhibitory protein to an activator of Wnt-signalling pathway by encouraging the transcription of the Wnt-responsive gene.[1]
Among cancer research, Wnt/β-catenin signalling is an area of focus since loss-of-function mutations in the APC gene results in β-catenin stabilization. Deletions within a chromosomal region containing the APC gene is understood to be associated with a hereditary disease known as familial adenomatous polyposis that yield intestinal polyps in large numbers that ultimately gives rise to tumors. Alternatively, mutations that promote gain-of-function of the APC gene inhibit the β-catenin destruction complex from limiting β-catenin concentrations in the cell. Additionally, some cancers have been correlated to a loss of Axin1 or Axin2 function. Overexpression of the Wnt/ β-catenin signalling pathway results in the constitutive activation of c-myc, and is most commonly linked to colorectal cancer.[2]
Since the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway plays a critical role in cancer, clinical research has yielded several new targets that may positively influence Wnt/β-catenin signalling where its absence is related to disease. Potential new drug targets include two lipid kinases that were found with the accumulation of β-catenin among HEK293T cells transfected with short inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) targeting human kinases, these include: (1) phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIα (PI4KIIα), and (2) phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type Iβ (PIP5Kiβ). Additionally, three human homologs of Drosophila PAR-1 can also provide useful drug targets as these elements activate Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway as well.[2]
There are many enzymes involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and knowing whether activation or repression is best suited will determine the molecular strategy to explore for therapeutic benefit.
