pour la recherche uniquement
Fludarabine inhibiteur de STAT1
Réf. CatalogueS1491
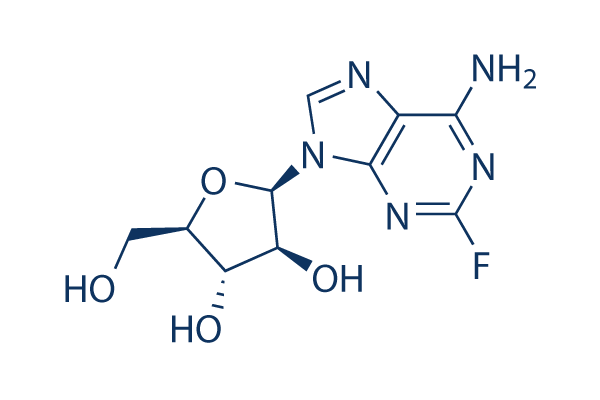
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 285.23
Contrôle Qualité
| Cibles apparentées | EGFR JAK Pim |
|---|---|
| Autre STAT Inhibiteurs | Napabucasin (BBI608) Stattic NSC 74859 (S3I-201) Cryptotanshinone (Tanshinone C) C188-9 (TTI-101) SH-4-54 BP-1-102 AS1517499 Nifuroxazide HO-3867 |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeko-1 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | inhibits expression of IDO | 25940712 | |
| MV-4-11 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| THP-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| MOLM 13 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30 μM | 25061101 | |||
| U2937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Mec-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50>500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Molt-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=180 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Nalm-6-FluR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=250 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Raji | Function Assay | 3 μM | 24/48/72 h | induces accumulations of p53, p63 and p73 | 24940695 | |
| PBMC | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits STAT1 phosphorylation | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNγ and LPS induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IRF1 expression | 24211327 | |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNα mediated phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3, but not of STAT2 | 24211327 | |
| BJAB | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| I-83 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| NALM6 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-10 μg/ml | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23734815 | |
| Nalm-6 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Reh | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| HEC1A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth slightly | 23595697 | |
| HEC1A | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 23595697 | |
| EHEB | Apoptosis Assay | 40 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23497075 | |
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7±2.8 µM | 23377192 | |||
| A549 GAPDH-deficient | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5±2.3 µM | 23377192 | |||
| CLL | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24-96 h | induces apoptotic cell death | 22207686 | |
| MEC1 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 μM | 72 h | induces apoptosis significantly | 22132973 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.8 μM | 4-48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22074700 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| Daudi | Apoptosis Assay | 20 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| J45.01 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 ± 3.7 μM | 21948264 | |||
| CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.4 ± 0.4 μM | 21948264 | |||
| Raji | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.47 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.24 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.44 ± 0.05 μM | 21948264 | |||
| NALM-6 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| JMV-3 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| EHEB | Function Assay | 5-50 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression significantly | 21168391 | |
| JVM-2 | Function Assay | 30 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression | 21168391 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=0.67 µM | 20933509 | |||
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.6 μM | 24 h | increases the cell fraction in S-phase | 20933509 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| HLE-B3 | Function Assay | 25 μM | 48 h | blocks IFN-γ–induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IDO expression | 20435158 | |
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=3.3 nM | 20307198 | ||
| BW-225 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| OH-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| GR-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=2.74 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=5.48 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| CaSki | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−7 μM | 18661380 | |||
| ZMK-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−6 μM | 18661380 | |||
| SKW6.4 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 24/48 h | induces cell death in both time- and dose- dependent manner | 18092340 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 24 h | IC50=1.54 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=13.48 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1R | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=33.79 μM | 17976186 | ||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3,200 ± 560 nM | 15930361 | |||
| CLL5 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL5 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.16 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human paclitaxel-resistant K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.26 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CLL3 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL3 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.35 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL4 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL4 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.64 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM-DNR-B | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM-DNR-B cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 1.01 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| primary CLL | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human primary CLL cells, LD50 = 1.1 μM. | 25148392 | |||
| CLL6 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL6 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 1.6 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL2 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL2 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 2.66 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 6.6 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| PBMC | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against patient PBMC after 48 hrs by CellTitre-Blue assay in presenc of mouse M210B4 cells, IC50 = 10 μM. | 25562417 | ||
| CHO | Function assay | Binding affinity determined by displacement of specific binding of [125I]N-(4-amino-3-iodophenethyl)-adenosine in membranes of CHO cells stably transfected with the rat adenosine A3 receptor, Ki = 10.4 μM. | 7707320 | |||
| JVM2 | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human JVM2 cells assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 10.4 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| HeLa | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human HeLa cells assessed as cell viability by MTT assay, EC50 = 16 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| CLL1 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL1 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 17.1 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 19.49 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| T47D | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human T47D cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 46.2 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 47.44 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Function assay | 10 uM | 1 to 60 mins | Drug transport in human CCRF-CEM cells assessed as ENT1-mediated uptake at 10 uM after 1 to 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting analysis | 23388705 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D caspase screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur la lignée cellulaire | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 285.23 | Formule | C10H12FN5O4 |
Stockage (À compter de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 21679-14-1 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | FaraA, Fludarabinum, NSC 118218 | Smiles | C1=NC2=C(N=C(N=C2N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)F)N | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 57 mg/mL
(199.83 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Saisir les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Saisir la formulation in vivo (Ceci est seulement le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouterμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouterμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouter μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouter μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Note : 1. Veuillez vous assurer que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue, lors de lajout précédent, est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie chaud peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
STAT1
(Vascular smooth muscle cells) |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Fludarabine inhibe efficacement la prolifération des cellules RPMI 8226 avec une IC50 de 1,54 μg/mL. L'IC50 de ce composé contre les cellules MM.1S et MM.1R est respectivement de 13,48 μg/mL et 33,79 μg/mL. En revanche, les cellules U266 sont résistantes à ce produit chimique avec une IC50 de 222,2 μg/mL. Le traitement par ce composé entraîne une augmentation du nombre de cellules en phase G1 du cycle cellulaire, accompagnée d'une réduction concomitante des cellules en phase S du cycle cellulaire de manière temps-dépendante. Il induit un blocage du cycle cellulaire et déclenche l'apoptose dans les cellules MM. Il déclenche le clivage temps-dépendant de la caspase-8, -9, et -3, -7, suivi du clivage de la PARP. Il augmente l'expression de Bax de manière temps-dépendante, tandis que l'expression de Bak ne change pas. Après une exposition à ce produit chimique pendant 12 heures, les cellules RPMI 8226 montrent une perte de potentiel membranaire avec 61,05% des cellules exprimant une faible fluorescence de la rhodamine 123 par rapport à 8,62% des cellules dans le contrôle non traité. Pour améliorer la solubilité, il est formulé sous forme de monophosphate (F-ara-AMP, fudarabine), qui est instantanément et quantitativement déphosphorylé en nucléoside parent après perfusion intraveineuse. À l'intérieur des cellules, une rephosphorylation se produit, ce qui conduit au triphosphate d'arabinoside de fluoroadénine (F-ara-ATP), le métabolite cytotoxique majeur de F-ara-A. Il peut également induire une stimulation pro-inflammatoire des cellules monocytaires, comme évalué par une augmentation de l'expression de l'ICAM-1 et de la libération d'IL-8. Ce composé n'affecte pas la croissance des lignées cellulaires de cancer de l'ovaire, alors qu'il induit une inhibition marquée et dose-dépendante de la prolifération dans les lignées cellulaires de mélanome. C'est un inhibiteur de STAT1 qui réduit spécifiquement STAT1 sans affecter les autres membres de la famille STAT. En plus de l'accumulation cytoplasmique, le cisplatine à faible dose répétée (RLDC) induit l'expression de HMGB1, qui est fortement supprimée par le knockdown de STAT1. De manière cohérente, ce produit chimique supprime l'expression de HMGB1 pendant le traitement RLDC de manière dose-dépendante dans les cellules tubulaires rénales traitées par RLDC. |
| In vivo |
Les tumeurs traitées avec du PBS se développent rapidement pour atteindre environ 10 fois leur volume initial en 25 jours, tandis que les tumeurs traitées avec Fludarabine à 40 mg/kg augmentent moins de 5 fois. Un effet antitumoral significatif de 40 mg/kg de ce composé sur la croissance tumorale de RPMI8226 est démontré. Les tumeurs RPMI8226 traitées avec 40 mg/kg de ce produit chimique au jour 10 augmentent les noyaux apoptotiques. Ce composé est efficace pour supprimer les xénogreffes de myélome RPMI8226 chez les souris SCID. |
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | procaspase-9 / procaspase-3 p-p53 / p53 STAT1 |
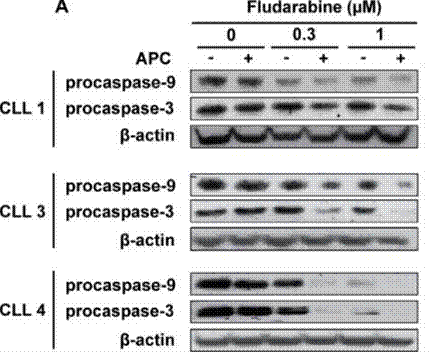
|
27223263 |
| Immunofluorescence | α-SMA / Vimentin |
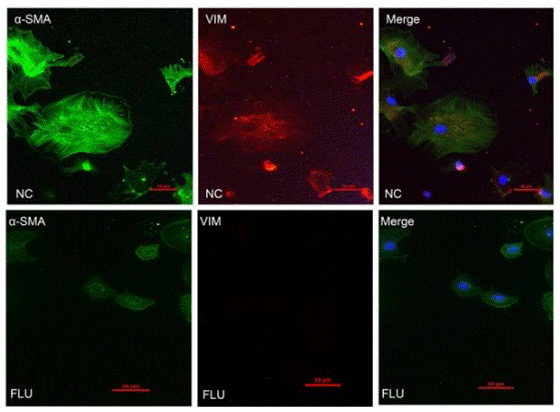
|
28322315 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
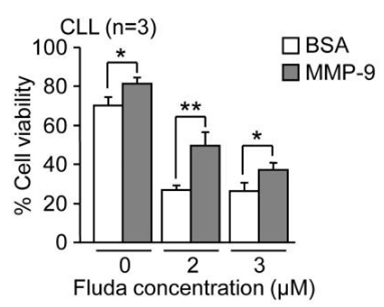
|
24956101 |
Informations sur lessai clinique
(données du https://clinicaltrials.gov, mis à jour le 2024-05-22)
| Numéro NCT | Recrutement | Conditions | Promoteur/Collaborateurs | Date de début | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05390814 | Recruiting | Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris |
December 18 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05201183 | Withdrawn | Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Chronic Myeloid Leukemia|Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia|Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Naoyuki G. Saito M.D. Ph.D.|Indiana University |
October 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05917405 | Recruiting | Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Remission |
Nantes University Hospital |
September 14 2023 | Phase 2 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
Foire aux questions
Question 1:
how to re-suspend and deliver it for in vivo experiments?
Réponse :
For S1491, we tested a vehicle: 30% Propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W that you can resuspend this compound in at up to 30mg/ml. It is a suspension and can only be given via oral gavage.
