pour la recherche uniquement
Saracatinib (AZD0530) Src inhibiteur
Réf. CatalogueS1006
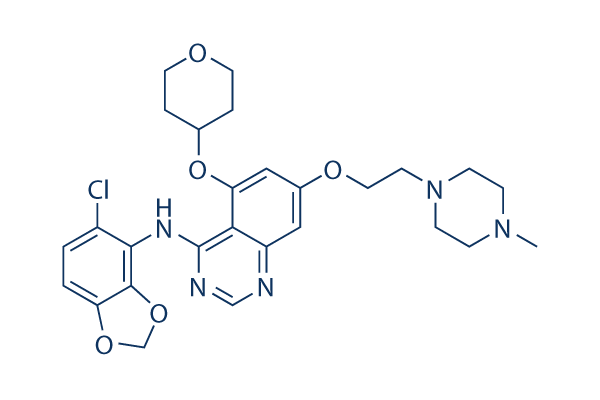
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 542.03
Contrôle Qualité
| Cibles apparentées | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 Bcr-Abl |
|---|---|
| Autre Src Inhibiteurs | WH-4-023 PP2 (AGL 1879) SU6656 PP1 Src Inhibitor 1 Tolimidone (MLR-1023) UM-164 1-Naphthyl PP1(1-NA-PP1) RK 24466 Myristic Acid |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.06143 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.1599 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEG-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.23688 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.265 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.27412 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.28116 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.3268 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.44196 μM | SANGER | |||
| K-562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.44967 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-336MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.50304 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.60529 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.62693 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.65249 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCCIT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.73218 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1436 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.79049 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB30-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.86203 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.87275 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.8921 μM | SANGER | |||
| TK10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.90669 μM | SANGER | |||
| KS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.19779 μM | SANGER | |||
| C2BBe1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.20507 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.2436 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.27687 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.37497 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.43418 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.44105 μM | SANGER | |||
| ST486 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.45852 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.50246 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.55083 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.55453 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66252 μM | SANGER | |||
| RL95-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66902 μM | SANGER | |||
| DOHH-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.71782 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFH-ino | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.7787 μM | SANGER | |||
| GB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.79833 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-DZ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.84688 μM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.88574 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.92093 μM | SANGER | |||
| KALS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.98722 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC24TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.05958 μM | SANGER | |||
| GI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.16084 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW962 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.17178 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW872 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.18507 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H747 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.25714 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ1-PC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.29356 μM | SANGER | |||
| MSTO-211H | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.35723 μM | SANGER | |||
| BL-70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.47422 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW954 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.57408 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNB75 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.68594 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.72379 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCIY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.87005 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.05299 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.12109 μM | SANGER | |||
| ETK-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.20767 μM | SANGER | |||
| SF126 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.31174 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC-2-ad | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.557 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-42 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.65 μM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.73433 μM | SANGER | |||
| PF-382 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.83698 μM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.25259 μM | SANGER | |||
| KM12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.32416 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.41864 μM | SANGER | |||
| KURAMOCHI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.65256 μM | SANGER | |||
| Becker | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.66416 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.81344 μM | SANGER | |||
| KINGS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.82373 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-123 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.49684 μM | SANGER | |||
| SF268 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.61262 μM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.63667 μM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.01811 μM | SANGER | |||
| CGTH-W-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.02075 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.53074 μM | SANGER | |||
| SR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.58807 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB49-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.73206 μM | SANGER | |||
| KLE | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.78377 μM | SANGER | |||
| HUTU-80 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.98466 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-C2B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.82737 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.94904 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.42808 μM | SANGER | |||
| GDM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.97292 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC4-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.00911 μM | SANGER | |||
| MLMA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.15006 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.30192 μM | SANGER | |||
| BOKU | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.96466 μM | SANGER | |||
| EVSA-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.6568 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-283MED | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.9176 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.0242 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8402 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.178 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.1806 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.3297 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-6666 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9567 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.2701 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5948 μM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9234 μM | SANGER | |||
| BE-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3915 μM | SANGER | |||
| SKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.4499 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.7591 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB771-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.7898 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.0277 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4655 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB647-SCLC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4949 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5256 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-540 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.8109 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2126 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.51 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0099 μM | SANGER | |||
| MPP-89 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.2289 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.8658 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.9255 μM | SANGER | |||
| EC-GI-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.5989 μM | SANGER | |||
| EKVX | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.0203 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC1TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.434 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daudi | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.0773 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.081 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.488 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9123 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-320-HSR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.0373 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.1287 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.7773 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC-1F | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.7346 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCLC-21H | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7317 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-PN-DW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5598 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-247MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.9773 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.0362 μM | SANGER | |||
| MONO-MAC-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.5048 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7666 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7928 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.144 μM | SANGER | |||
| A253 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7429 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1599 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.7053 μM | SANGER | |||
| EB-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.9518 μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.3224 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.8495 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.0522 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.1676 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.4596 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.3925 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.5034 μM | SANGER | |||
| RCC10RGB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.7392 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP67-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.6241 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB17 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.6643 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-UT-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.9464 μM | SANGER | |||
| JiyoyeP-2003 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0119 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCE-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.5968 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7682 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-422 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.0895 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.1622 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCE-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.6828 μM | SANGER | |||
| PSN1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.7813 μM | SANGER | |||
| NIH3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of human c-Src in NIH3T3 cells, IC50 = 0.0027 μM. | 17064066 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of human full length PKMYT1 expressed in HEK293 cells using EFS (247 to 259 residues) as substrate after 1 hr by fluorescence polarization immunoasay, Ki = 0.0398 μM. | 29941193 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of human full length PKMYT1 expressed in HEK293 cells using EFS (247 to 259 residues) as substrate after 1 hr by fluorescence polarization immunoasay, IC50 = 0.418 μM. | 29941193 | ||
| Rh30 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human Rh30 cells after 48 hrs by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 10.1 μM. | 23787099 | ||
| Huh7 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 5 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected human Huh7 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 5 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| Huh7 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 6 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected human Huh7 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 6 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| Vero | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 4 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected african green monkey Vero cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 4 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| Vero | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 6 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected african green monkey Vero cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 6 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| C6/36 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 4 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected asian tiger mosquito C6/36 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 4 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| C6/36 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 5 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected asian tiger mosquito C6/36 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 5 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| Vero | Antiviral assay | 3 days | Antiviral activity against Dengue virus infected in african green monkey Vero cells administered after viral challenge after 3 days by viral plaque assay | 17360676 | ||
| Vero | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 5 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected african green monkey Vero cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 5 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| Huh7 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 4 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected human Huh7 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 4 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| C6/36 | Antiviral assay | 2.5 uM | 6 days | Inhibition of viral spread in Dengue virus-infected asian tiger mosquito C6/36 cells assessed as accumulation of viral envelope protein within perinuclear region at 2.5 uM after 6 days by immunofluorescence assay relative to control | 17360676 | |
| HEK293 | Function assay | 0.1 to 1 uM | 16 hrs | Inhibition of collagen I-induced DDR2 (unknown origin) phosphorylation expressed in HEK293 cells at 0.1 to 1 uM after 16 hrs by Western blotting | 26191369 | |
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 0.1 to 1 uM | 16 hrs | Inhibition of collagen I-induced DDR2 I638F mutant (unknown origin) phosphorylation expressed in HEK293 cells at 0.1 to 1 uM after 16 hrs by Western blotting | 26191369 | |
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur la lignée cellulaire | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 542.03 | Formule | C27H32ClN5O5 |
Stockage (À compter de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 379231-04-6 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | N/A | Smiles | CN1CCN(CC1)CCOC2=CC3=C(C(=C2)OC4CCOCC4)C(=NC=N3)NC5=C(C=CC6=C5OCO6)Cl | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(184.49 mM)
Ethanol : 100 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Saisir les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Saisir la formulation in vivo (Ceci est seulement le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouterμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouterμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouter μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouter μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Note : 1. Veuillez vous assurer que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue, lors de lajout précédent, est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie chaud peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Caractéristiques |
The 1st Src inhibitor to show inhibition of the Src pathway in human tumor tissue.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
c-Src
(Cell-free assay) 2.7 nM
LCK
(Cell-free assay) <4 nM
c-YES
(Cell-free assay) 4 nM
EGFR (L861Q)
(Cell-free assay) 4 nM
Lyn
(Cell-free assay) 5 nM
EGFR (L858R)
(Cell-free assay) 5 nM
Fyn
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM
FGR
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM
BLK
(Cell-free assay) 11 nM
v-Abl
(Cell-free assay) 30 nM
EGFR
(Cell-free assay) 66 nM
c-Kit
(Cell-free assay) 200 nM
EphA2
(Cell-free assay) 236 nM
|
| In vitro |
Le Saracatinib (AZD0530) inhibe également puissamment d'autres membres de la famille des tyrosine kinases Src, y compris c-Yes, Fyn, Lyn, Blk, Fgr et Lck avec des IC50 de 4 à 10 nM. Il inhibe de manière sensible Src Y530F NIH 3T3 avec une IC50 de 80 nM. Ce composé altère significativement l'invasion des cellules HT1080 à travers une matrice de collagène tridimensionnelle et inhibe complètement la dispersion cellulaire induite par l'EGF dans les cellules de cancer de la vessie NBT-II. Il inhibe puissamment l'activation de Src dans les cellules DU145 et PC3, par inhibition de la phosphorylation de Y419. Il inhibe la croissance des cancers de la prostate, y compris PC3, DU145, CWR22Rv1 et LNCaP, tout en montrant une faible activité dans les cellules LAPC-4, PZ-HPV7 et RWPE-1. Il induit un arrêt du cycle cellulaire en G1/S mais pas les clivages de la caspase 3. Il inhibe également significativement la migration des DU145 et PC3 dans la chambre de Boyden. Il provoque un blocage puissant et soutenu d'AKT et améliore la sensibilité à l'irradiation dans les cellules A549 et Calu-6. Il inhibe l'ostéoclaste en activité, résorption et formation. Il empêche également de manière réversible la migration des précurseurs d'ostéoclastes. |
| Essai kinase |
Essai Kinase
|
|
L'IC50 de l'activité tyrosine kinase est mesurée par un dosage immunoenzymatique (ELISA) avec des domaines catalytiques recombinants d'un panel de récepteurs et de tyrosine kinases non-récepteurs (dans certains cas, seule une partie du domaine catalytique est utilisée). Ce composé est dosé dans une gamme de 0,001 à 10 mM. Des dosages de spécificité contre un panel de sérine/thréonine kinases sont réalisés à l'aide d'un essai de capture sur filtre avec du 32P. En bref, des plaques 384 puits multidrop contenant 0,5 μL de Saracatinib (AZD0530) ou des contrôles (DMSO seul ou contrôles tampon pH 3,0) sont incubées avec 15 μL d'enzyme plus substrat peptidique/protéique pendant 5 min avant que la réaction ne soit initiée par l'ajout de 10 μL de 20 mM Mg-ATP. Pour toutes les enzymes, la concentration finale est approximée à la constante de Michaelis (Km). Les essais sont réalisés pendant 30 min à température ambiante avant l'arrêt par l'ajout de 5 μL d'acide orthophosphorique. Après mélange, le contenu des puits est recueilli sur une plaque P81 Unifilter, en utilisant de l'acide orthophosphorique comme tampon de lavage. L'IC50 est ensuite calculée.
|
|
| In vivo |
Le Saracatinib (AZD0530) montre une grande inhibition de la croissance tumorale dans les allogreffes Src3T3 et un délai de croissance modéré dans les xénogreffes Calu-6, MDA-MB-231, AsPc-1 et BT474C. Ce composé montre également une grande activité antitumorale chez les souris xénogreffées orthotopiques DU145 à une dose de 25 mg/kg (administrée oralement, quotidiennement). |
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
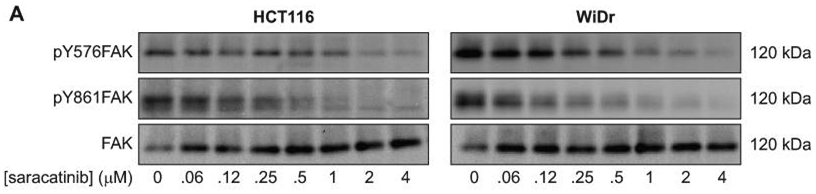
| Western blot | pY576-FAK / pY861-FAK / FAK pY418 Src / Src / pY410 CAS / CAS / Py421 Cortactin / Cortactin p-Akt / p-mTOR / Akt / mTOR / p-S6 / S6 / p-AMPKα / AMPKα |
|
20551056 |
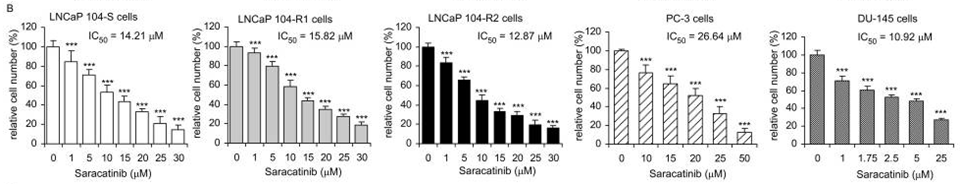
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell number |
|
24349321 |
Informations sur lessai clinique
(données du https://clinicaltrials.gov, mis à jour le 2024-05-22)
| Numéro NCT | Recrutement | Conditions | Promoteur/Collaborateurs | Date de début | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04598919 | Active not recruiting | Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) |
National Jewish Health|Yale University|Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai|AstraZeneca|National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)|Baylor University|International Center for Health Outcomes and Innovation Research |
November 12 2020 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04307953 | Recruiting | Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva |
Amsterdam UMC location VUmc|Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust|Klinikum Garmisch-Patenkirchen|University of Oxford|Brigham and Women''s Hospital|AstraZeneca|Innovative Medicines Initiative |
August 5 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02085603 | Completed | Cancer |
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust|AstraZeneca |
March 2014 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01864655 | Completed | Alzheimer''s Disease |
Stephen M. Strittmatter|National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)|Yale University |
July 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01000896 | Withdrawn | Cancer|Non Small Cell Lung Cancer|Epithelial Ovarian Cancer |
AstraZeneca |
January 2010 | Phase 1 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
Foire aux questions
Question 1:
What is its half-life?
Réponse :
Based on the following paper, its half-life in vivo is around 40 hours and it reaches its peak level around 2–4 hours after dosing: http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/16/19/4876.long
