pour la recherche uniquement
SB216763 GSK-3 inhibiteur
Réf. CatalogueS1075
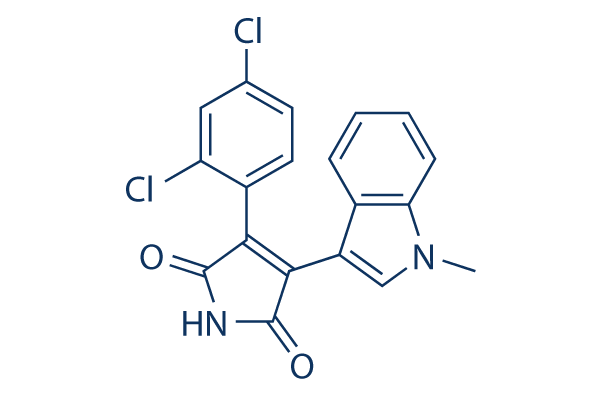
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 371.22
Contrôle Qualité
| Cibles apparentées | PI3K Akt mTOR ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Autre GSK-3 Inhibiteurs | CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) Hydrochloride CHIR-98014 TWS119 GSK-3 Inhibitor IX (BIO) LY2090314 Tideglusib SB415286 AR-A014418 IM-12 |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | Function assay | Glycogen synthase activity of HEK293 cells, inhibition of GSK3-beta, EC50=0.2μM | 12941331 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Effective concentration of compound against glycogen synthase kinase-3 in HEK293 cells, EC50=0.2μM | 15149684 | |||
| MIAPaCa2 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MIAPaCa2 cells after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=25μM | 19338355 | ||
| ST14A | Function assay | 6 hrs | Inhibition of GSK-3-beta-mediated Wnt signaling in human ST14A cells assessed as increase in accumulation of beta-casein around nucleus after 6 hrs by microscopic analysis | 20708937 | ||
| neural precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of neurosphere proliferation of mouse neural precursor cells by MTT assay | 17417631 | |||
| ReNcell VM | Antiproliferative assay | 3 uM | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human ReNcell VM cells assessed as reduction of cell proliferation at 3 uM after 72 hrs | 20708937 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Increase in glucose incorporation in human HepG2 cells at 34 uM after 12 hrs by glucose assay | 25467150 | |
| 3T3L1 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Increase in glucose incorporation in mouse 3T3L1 cells at 34 uM after 12 hrs by glucose assay | 25467150 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of GSK3beta in human HepG2 cells assessed as decrease in ratio of phosphorylated GS/GS at 34 uM after 12 hrs by Western blot analysis | 25467150 | |
| Sf9 | Function assay | 30 min | Inhibition of GSK3beta (unknown origin) expressed in Sf9 cells using GS1 as substrate and [gamma32]ATP after 30 min by scinitllation counting, IC50=0.03388μM | SANGER | ||
| human HDLM-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HDLM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.20984 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1770 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1770 cell growth in a cell viability assay. IC50=0.29392 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HOP-62 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HOP-62 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.85256 μM | SANGER | |||
| human JAR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human JAR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.21044 μM | SANGER | |||
| human K5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human K5 cell growth in a cell viability, IC50=1.53698 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MV-4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MV-4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.69685 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BT-549 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BT-549 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=5.29376 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LB2241-RCC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LB2241-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.42874 μM | SANGER | |||
| human GAMG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GAMG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.65409 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HMV-II cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HMV-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=7.67607 μM | SANGER | |||
| human RS4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RS4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.24141 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1993 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1993 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.36534 μM | SANGER | |||
| human IST-SL1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IST-SL1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.0204 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-OV-3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-OV-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.1002 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ESS-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ESS-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.59872 μM | SANGER | |||
| human G-361 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human G-361 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=10.1798 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ALL-PO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ALL-PO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=10.3477 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NB5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.2157 μM | SANGER | |||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.6535 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NMC-G1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NMC-G1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.7264 μM | SANGER | |||
| human RPMI-7951 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RPMI-7951 cell growth in a cell viability assay. IC50=11.7864 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H2009 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2009 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.2427 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LoVo cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LoVo cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.3771 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A2058 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A2058 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.469 μM | SANGER | |||
| human D-566MG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human D-566MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.9481 μM | SANGER | |||
| human QIMR-WIL cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human QIMR-WIL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.6394 μM | SANGER | |||
| human S-117 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human S-117 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.4022 μM | SANGER | |||
| human YH-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human YH-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.6865 μM | SANGER | |||
| human IGROV-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IGROV-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.2001 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BHT-101 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHT-101 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.6099 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MKN45 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MKN45 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=18.4128 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A498 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A498 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.4549 μM | SANGER | |||
| human U-266 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U-266 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.8797 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BFTC-905 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BFTC-905 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.1879 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BxPC-3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BxPC-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.3554 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-SNU-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-SNU-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.5558 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SF539 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SF539 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.0198 μM | SANGER | |||
| human VA-ES-BJ cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human VA-ES-BJ cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.5763 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HuO-3N1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HuO-3N1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.6151 μM | SANGER | |||
| human EM-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.6689 μM | SANGER | |||
| human T98G cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human T98G cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.3009 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1783 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1783 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.5243 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NKM-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NKM-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.8512 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KOSC-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KOSC-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.1292 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW48 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW48 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.6067 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H28 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H28 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=25.2104 μM | SANGER | |||
| human 5637 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 5637 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=25.8111 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NB69 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB69 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=26.1764 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HT-29 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HT-29 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.1752 μM | SANGER | |||
| human PFSK-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PFSK-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.593 μM | SANGER | |||
| human UACC-257 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human UACC-257 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.743 μM | SANGER | |||
| human D-423MG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human D-423MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9106 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NH-12 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NH-12 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=28.4059 μM | SANGER | |||
| human DEL cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DEL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.0474 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LS-513 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LS-513 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.1334 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NBsusSR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NBsusSR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.5678 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BV-173 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BV-173 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.7649 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A101D cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A101D cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.9784 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LU-134-A cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LU-134-A cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=31.0238 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ES3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ES3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=31.3376 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.2965 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1975 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1975 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.3582 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A704 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A704 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2059 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-MEL-24 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-24 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2523 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1088 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1088 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.3452 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-MEL-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-1 cell growth in a cell viability, IC50=34.714 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MOLT-4 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MOLT-4 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.1467 μM | SANGER | |||
| human T47D cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human T47D cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.1647 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1710 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1710 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.3608 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MKN7 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MKN7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.0909 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-72 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-72 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.1178 μM | SANGER | |||
| human AGS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AGS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.2039 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BE-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BE-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.7783 μM | SANGER | |||
| human Calu-6 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Calu-6 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=39.6964 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-27 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-27 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.0054 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BB49-HNC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BB49-HNC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.0278 μM | SANGER | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur la lignée cellulaire | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 371.22 | Formule | C19H12N2O2Cl2 |
Stockage (À compter de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 280744-09-4 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | N/A | Smiles | CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)C3=C(C(=O)NC3=O)C4=C(C=C(C=C4)Cl)Cl | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 23 mg/mL
(61.95 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Saisir les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Saisir la formulation in vivo (Ceci est seulement le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouterμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouterμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouter μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouter μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Note : 1. Veuillez vous assurer que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue, lors de lajout précédent, est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie chaud peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GSK-3α
(Cell-free assay) 34.3 nM
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) ~34.3 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Le SB 216763 présente une puissance similaire pour la GSK-3β avec 96 % d'inhibition à 10 μM, tout en présentant une activité minimale contre 24 autres protéine kinases, y compris PKBα et PDK1 avec une IC50 > 10 μM. Ce composé stimule la synthèse du glycogène dans les cellules hépatiques humaines avec une EC50 de 3,6 μM, et induit une transcription dose-dépendante d'un gène rapporteur régulé par la β-caténine-LEF/TCF dans les cellules HEK293 avec une induction maximale de 2,5 fois à 5 μM. Il protège les neurones granulaires du cervelet de la mort cellulaire apoptotique induite par le LY-294002 ou la privation de potassium de manière concentration-dépendante, avec une neuroprotection maximale à 3 μM, contrairement à l'effet du chlorure de lithium qui nécessite 10 mM. Ce produit chimique à 3 μM prévient également complètement la mort des neurones sensoriels des ganglions rachidiens dorsaux de poulet induite par le LY-294002, indépendamment du NGF. Son traitement à 5 μM inhibe fortement la phosphorylation dépendante de la GSK-3 de la protéine tau associée aux microtubules spécifique aux neurones dans les neurones granulaires du cervelet ou de la tau recombinante dans les cellules HEK293, et induit une augmentation des niveaux de β-caténine cytoplasmique dans les deux cellules, mimant l'effet de l'inhibition de la GSK-3 médiée par Wnt. Dans les lignées cellulaires de cancer du pancréas, y compris BXPC-3, MIA-PaCa2, PANC1, ASPC1 et CFPAC, le traitement avec ce composé à 25-50 μM réduit la viabilité cellulaire de manière dose-dépendante et entraîne une augmentation significative de l'apoptose de 50 % à 72 heures en raison de la régulation négative spécifique de la GSK-3β, tandis qu'il n'a aucun effet sur les lignées cellulaires HMEC ou WI38.
|
| Essai kinase |
dosage d'activité de la GSK-3
|
|
L'activité de la kinase GSK-3 est mesurée, en présence de diverses concentrations de SB 216763, dans un mélange réactionnel contenant des concentrations finales de 1 nM de GSK-3α humaine, 50 mM de MOPS pH 7,0, 0,2 mM d'EDTA, 10 mM d'acétate de Mg, 7,5 mM de β-mercaptoéthanol, 5 % (p/v) de glycérol, 0,01 % (p/v) de Tween-20, 10 % (v/v) de DMSO et 28 μM de substrat peptidique GS-2. La séquence peptidique GS-2 correspond à une région de la glycogène synthase qui est phosphorylée par la GSK-3. Le test est initié par l'ajout de 0,34 μCi de [33P]γ-ATP. La concentration totale d'ATP est de 10 μM. Après 30 minutes d'incubation à température ambiante, le test est arrêté par l'ajout d'un tiers du volume du test de 2,5 % (v/v) de H3PO4 contenant 21 mM d'ATP. Les échantillons sont déposés sur des tapis de phosphocellulose P30 et lavés six fois dans 0,5 % (v/v) de H3PO4. Les tapis filtrants sont scellés dans des sacs d'échantillons contenant du liquide de scintillation Wallac betaplate. L'incorporation de 33P dans le peptide substrat est déterminée en comptant les tapis dans un compteur à scintillation Wallac microbeta.
|
|
| In vivo |
L'administration de SB 216763 à 20 mg/kg prévient de manière significative l'inflammation pulmonaire et la fibrose subséquente dans un modèle murin d'inflammation et de fibrose pulmonaire induite par la bléomycine (BLM) en bloquant significativement la production de cytokines inflammatoires MCP-1 et TNF-α par les macrophages, et améliore significativement la survie des souris traitées par la BLM. Ce traitement composé entraîne une réduction significative de l'alvéolite induite par la BLM en inhibant les dommages aux cellules épithéliales alvéolaires.
|
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | c-Myb pGSK-3β / GSK-3β / E2F1 / β-catenin |

|
21795403 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
24779365 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
