AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular energy homeostasis as the principal energy sensor in most eukaryotic cells. In response to stress, AMPK activation switches on catabolic pathways that generate ATP while simultaneously inactivating biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP. [show the full text]
AMPK activateurs/inhibiteurs (AMPK Activators/Inhibitors)
| N° Cat. | Nom du produit | Information | Citations dutilisation du produit | Validations de produits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
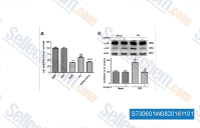
| S7306 | Dorsomorphin Dihydrochloride | Le Dorsomorphin 2HCl est un inhibiteur puissant, réversible et sélectif de l'AMPK avec un Ki de 109 nM dans des essais acellulaires, n'exhibant aucune inhibition significative de plusieurs kinases structurellement apparentées, y compris ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA et JAK3. Il inhibe également l'activité du récepteur de type I BMP. La Dorsomorphin induit l'autophagy dans les lignées de cellules cancéreuses. |
|
|
| S1208 | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Hydrochloride | Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl est un agent antibiotique qui inhibe la DNA topoisomerase II humaine avec un IC50 de 2,67 μM. La Doxorubicin réduit la phosphorylation basale de l'AMPK. La Doxorubicin est utilisée dans le traitement concomitant des patients infectés par le HIV mais s'avère être à haut risque de réactivation du VHB.Ce produit peut précipiter lorsqu'il est dissous dans une solution de PBS. Il est recommandé de préparer la solution mère dans de l'eau pure et de la diluer avec de l'eau pure ou une solution saline pour obtenir la solution de travail.Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl peut être utilisé pour induire des modèles animaux de maladie rénale. |
|
|
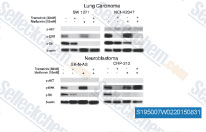
| S1950 | Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride (Chlorhydrate de 1,1-Diméthylbiguanide) est un agent Antihyperglycémique très efficace, qui diminue principalement l'hyperglycémie dans les hépatocytes en supprimant la néoglucogenèse hépatique (production de glucose par le foie). Il favorise également la Mitophagy dans les cellules mononucléées et induit l'apoptose des cellules cancéreuses du poumon en activant la voie JNK/p38 MAPK et GADD153. |
|
|
| S8161 | ON123300 | ON123300 est un inhibiteur de kinase puissant et multi-ciblé avec des IC50 de 3,9 nM, 5 nM, 26 nM, 26 nM, 9,2 nM et 11 nM pour CDK4, Ark5/NUAK1, PDGFRβ, FGFR1, RET (c-RET) et Fyn, respectivement. |
|
|
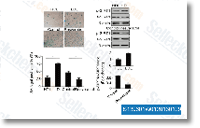
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Le Resveratrol a un large spectre de cibles incluant les cyclooxygénases (c.-à-d. la COX, IC50=1.1 μM), les lipooxygénases (LOX, IC50=2.7 μM), les kinases, les sirtuines et d'autres protéines. Il a des effets anticancéreux, anti-inflammatoires, hypoglycémiants et d'autres effets cardiovasculaires bénéfiques. Le Resveratrol induit la mitophagie/autophagie et l'apoptose dépendante de l'autophagie. |
|
|
| S7840 | Dorsomorphin (Compound C) | La Dorsomorphine est un inhibiteur puissant, réversible et sélectif de l'AMPK avec un Ki de 109 nM dans des essais sans cellules, n'exhibant aucune inhibition significative de plusieurs kinases structurellement apparentées, y compris ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA et JAK3. La Dorsomorphine inhibe sélectivement les récepteurs de type I de BMP ALK2, ALK3 et ALK6. La Dorsomorphine est utilisée pour promouvoir une différenciation cellulaire spécifique et induire l'autophagie des lignées de cellules cancéreuses. Pour les tests cellulaires, la S7306 Dorsomorphin (Composé C) 2HCl hydrosoluble est recommandée. |
|
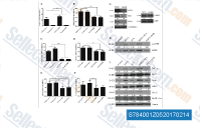
|
| S1802 | AICAR (Acadesine) | L'AICAR (Acadesine, NSC105823, AICA Riboside), un activateur de l'AMPK, entraîne une accumulation de ZMP, qui imite l'effet stimulant de l'AMP sur l'AMPK et l'AMPK kinase. Ce composé induit la mitophagy. Phase 3. |
|
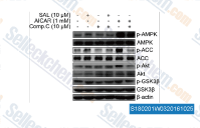
|
| S2697 | A-769662 | Le A-769662 est un activateur puissant et réversible de l'AMPK avec un EC50 de 0,8 μM dans les tests sans cellules, ayant peu d'effet sur l'activité GPPase/FBPase. |
|
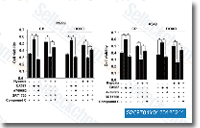
|
| S5958 | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide) | La Metformin (1,1-diméthylbiguanide), un médicament largement utilisé pour le traitement du diabète de type 2, active la protéine kinase activée par l'AMP (AMPK) dans les hépatocytes. La Metformin favorise la mitophagy dans les cellules mononucléaires. La Metformin induit l'apoptose des cellules cancéreuses du poumon en activant la voie JNK/p38 MAPK et GADD153. |
|
|
| S7898 | GSK621 | Le GSK621 est un activateur de l'AMPK spécifique et puissant. |
|
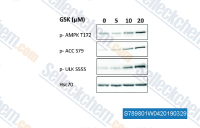
|
AMPK exists as a heterotrimeric protein complex composed of a catalytic α-subunit (α1 or α2) and regulatory β-subunit (β1 or β2) and γ- subunit (γ1, γ2 or γ3). The structure of the α-subunit consists of a conventional Ser/Thr kinase domain at the N-terminal, an auto-inhibitory domain (AID), an extended linker peptide and the α-subunit C-terminal domain (α-CTD). The β-subunit contains a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), with the β-subunit C-terminal domain (β-CTD) interacting with both the α-CTD and the amino terminus of the γ-subunit, thus forming the core of the complex. The γ-subunit includes four tandem repeats of a sequence motif, termed a CBS repeat (cystathionine β-synthase, CBS1-4), that forms a flattened disk with one repeat in each quadrant to create four potential ligand binding sites in the centre (site 1-4). AMPK activity increases more than 100-fold when the conserved Thr172 residue in the activation loop of the catalytic α-subunit is phosphorylated by upstream AMPK kinases (AMPKK) such as LKB1 requiring the change in AMP or ADP levels, and CaMKKβ (CaMKK2) in response to increases in cell Ca2+. AMP binding to ligand binding site 1 of the γ subunit allosterically activates the AMPK complex by facilitating the phosphorylation of Thr172 in the catalytic α-subunit, whereas binding of AMP or ADP to site 3 modulates the phosphorylation state of Thr172. In addition to allosteric activation by AMP, the effects on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Thr172 can also be produced by ADP, which requires N-terminal myristylation of the β-subunit. [1][2]
AMPK is activated by various types of metabolic stress (glucose deprivation, hypoxia, ischemia, metabolic poisons, or muscle contraction), as well as drugs and xenobiotics (metformin, resveratrol, or berberine) through the classical or canonical mechanisms, which involve increases in cellular AMP, ADP or Ca2+. The metformin for the treatment of people with type 2 diabetes indirectly activates AMPK by increasing cellular AMP and ADP, usually by inhibiting mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Additionally, AMPK activated by resveratrol or metformin upregulates genes involved in oxidative metabolism and oxidative stress resistance by regulating transcription factors of the abnormal dauer formation 16 (DAF-16)/forkhead box O (FOXO) family, contributing to its effects on extending healthy lifespan. Some types of cellular stress such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damaging agents (etoposide, doxorubicin and ionizing radiation) activate AMPK by non-canonical mechanisms that involve ATM rather than the increases in AMP, ADP or Ca2+ levels. Activation of AMPK enhances both the transcription and translocation of GLUT4, resulting in an increase in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. In LKB1-knockout but not AMPKα1-knockout mice, the effects of both AICAR and contraction on glucose uptake are lost. In addition, AMPK also stimulates other catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis via inhibition of ACC2 and activation of PFKFB. AMPK is also involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of PGC1α, and the turnover of mitochondria via the special form of autophagy termed mitophagy by activating ULK1, and subsequently triggering autophagy. In addition, mTOR complex-1 (TORC1) can be inhibited by AMPK mediated phosphorylation of both its upstream regulator, TSC2, and the TORC1 subunit Raptor. Consistent with its role in cellular energy homeostasis, AMPK also conserves ATP by switching off almost all anabolic pathways, including the biosynthesis of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and ribosomal RNA. Moreover, AMPK also functions beyond metabolism through regulation of the cell cycle and modulation of membrane excitability. As LKB1 is a tumor suppressor and is frequently mutated in spontaneous cancers, AMPK-activating drugs such as metformin or A-769662 significantly protect against the development of cancer. [1][2]
