pour la recherche uniquement
JNK Inhibitor VIII JNK inhibiteur
Réf. CatalogueS7794
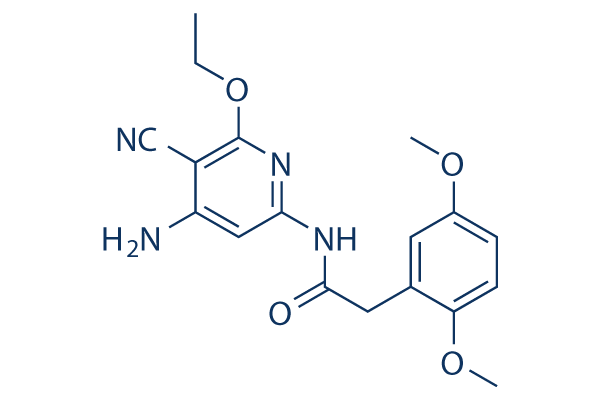
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 356.38
Contrôle Qualité
- Cité dans Nature Medicine pour sa qualité supérieure
- COA
- NMR
- SDS
- Fiche technique
| Cibles apparentées | ERK p38 MAPK Raf MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Autre JNK Inhibiteurs | CC-90001 SP600125 JNK-IN-8 Anisomycin (Flagecidin) JNK Inhibitor IX Tanzisertib Hydrochloride (CC-930) Polyphyllin I DTP3 BI-78D3 Bentamapimod (AS602801) |
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB7 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.27473μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LB2241-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.57739μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1299 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1299 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.2019μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BV-173 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=14.0505μM | SANGER | |||
| HPAF-II | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HPAF-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=14.5873μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RS4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.6795μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EW-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.1883μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1581 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1581 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.2588μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-PN-DW | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-PN-DW cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.9485μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KP-4 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.1087μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.8748μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ACHN cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.6213μM | SANGER | |||
| A172 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A172 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.263μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HuO-3N1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.4318μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human QIMR-WIL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.3274μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1650 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.7873μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1088 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1088 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.1641μM | SANGER | |||
| Mewo | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Mewo cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.3997μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1355 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.6365μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-LU-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.058μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-70 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-70 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.125μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KP-N-YS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.5706μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HTC-C3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.7345μM | SANGER | |||
| NB17 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB17 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9113μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GOTO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9415μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BEN cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.865μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HMV-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.1553μM | SANGER | |||
| SF295 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SF295 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.156μM | SANGER | |||
| MPP-89 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MPP-89 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=33.5199μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-103H | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LCLC-103H cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2223μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MN-60 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.0139μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BB65-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.1528μM | SANGER | |||
| BHY | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.9645μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.7324μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.7592μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-72 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.9289μM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ES3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.1949μM | SANGER | |||
| NBsusSR | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NBsusSR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=39.3132μM | SANGER | |||
| NB10 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB10 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=40.1731μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ChaGo-K-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.1576μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-450 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-450 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.4514μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.9927μM | SANGER | |||
| PC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PC-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=42.2752μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KARPAS-299 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.5948μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DBTRG-05MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.6546μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCC1806 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.2169μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2009 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2009 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.2843μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCC2157 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.7976μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=47.4011μM | SANGER | |||
| DOK | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DOK cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=48.3877μM | SANGER | |||
| HepG2 | Function assay | Inhibition of cJun phosphorylation in HepG2 cell line, Ki=0.004μM | 16759099 | |||
| HepG2 | Function assay | Inhibition of cJun phosphorylation in HepG2 cell line, EC50=0.92μM | 16759099 | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur la lignée cellulaire | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 356.38 | Formule | C18H20N4O4 |
Stockage (À compter de la date de réception) | 3 years -20°C powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 894804-07-0 | -- | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | TCS JNK 6o | Smiles | CCOC1=C(C(=CC(=N1)NC(=O)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)OC)OC)N)C#N | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 71 mg/mL
(199.22 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Saisir les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Saisir la formulation in vivo (Ceci est seulement le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouterμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouterμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouter μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouter μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Note : 1. Veuillez vous assurer que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue, lors de lajout précédent, est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie chaud peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
JNK1
(Cell-free assay) 2 nM(Ki)
JNK2
(Cell-free assay) 4 nM(Ki)
JNK1
(Cell-free assay) 45 nM
JNK3
(Cell-free assay) 52 nM(Ki)
JNK2
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
JNK Inhibitor VIII (TCS-JNK-6a) se lie de manière compétitive et réversible au site ATP. Ce composé présente un profil de sélectivité remarquable. De plus, il montre une certaine inhibition de la phosphorylation de c-Jun dans les cellules HepG2. Le TCS-JNK-6o est un analogue 2,5-diméthoxy de cette substance chimique avec la substitution diméthoxy du cycle phényle. Ce composé montre des gains supplémentaires en puissance. |
| Essai kinase |
Ser/Thr-kinase
|
|
Les dosages de Ser/Thr-kinase sont réalisés en utilisant une plateforme de dosage radioactive basée sur FlashPlate. Dans ce format, le peptide substrat biotinylé (2 μM), le γ-[33P]-ATP (5 μM, 2 mCi/μmol), ce composé (3-10000 nM dans 2% de DMSO) et l'enzyme sont incubés pendant 1 h dans un tampon contenant 25 mM Hepes, pH 7,5, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM MgCl2, 100 μM Na3VO4 et 0,075 mg/mL Triton X-100, arrêtés avec 80 μL de tampon d'arrêt contenant 100 mM EDTA et 4 M NaCl, transférés sur des FlashPlates à 384 puits revêtues de streptavidine, qui sont ensuite lavées 3 fois et lues à l'aide d'un lecteur de microplaques TopCount.
|
|
| In vivo |
Les profils pharmacocinétiques sont déterminés pour JNK Inhibitor VIII (TCS-JNK-6o) chez des rats Sprague-Dawley. Ce composé montre une courte demi-vie d'environ 1 h, avec une clairance rapide et une biodisponibilité à peine mesurable. Des études d'incubation microsomales ont révélé que le métabolisme oxydatif est très rapide avec ce composé. |
Références |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
