pour la recherche uniquement
Ganetespib (STA-9090) HSP90 Inhibitor
Réf. CatalogueS1159
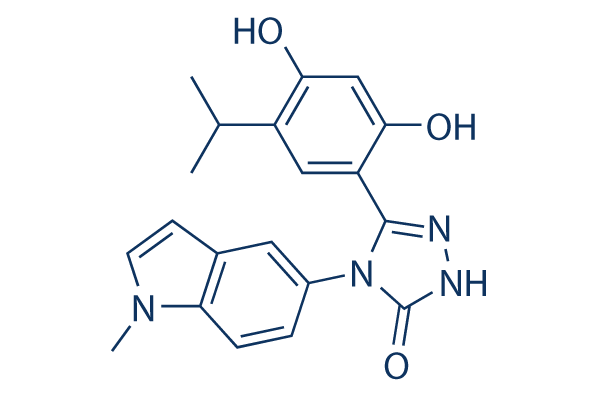
Structure chimique
Poids moléculaire: 364.4
Contrôle Qualité
Culture cellulaire, traitement et concentration de travail
| Lignées cellulaires | Type dessai | Concentration | Temps dincubation | Formulation | Description de lactivité | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=8 nM | 22144665 | ||
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=16 nM | 22144665 | ||
| Calu-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=64 nM | 23012248 | |||
| Calu-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2122 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 23012248 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1734 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2009 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19 nM | 23012248 | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2212 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H441 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2030 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H460 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1355 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 23012248 | |||
| VCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23152004 | |||
| LNCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23152004 | |||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Karpas-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (2) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (1) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RS4;11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-136 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-90 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-1643 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-258 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| TC-71 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-266 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.1 nM | 23303741 | |||
| BT-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh41 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| K033 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K033 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces a modest increase in G1 population | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 and G2/M arrest | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K033 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=75.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| M23 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=37.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K029 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=46 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K028 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=84 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K008 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=60 nM | 23418523 | |||
| H3122 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=10 nM | 23533265 | |
| H2228 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=13 nM | 23533265 | |
| A1847 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| SKOV-3 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| A1847 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| H146 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| GLC4 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| H82 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| AC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H1173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.62 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.07 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.67 nM | 24166505 | |||
| N592 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.12 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.64 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.99 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H146 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.51 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H128 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=69.55 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=83.36 nM | 24166505 | |||
| GLC4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.47 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.27 nM | 24166505 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 24 h | inhibits the migratory and invasive capacity | 24173541 | |
| BT-20 | Function Assay | 100/250 nM | 24 h | resulted in a dose-dependent destabilization of EGFR, IGF-IR, MET, and CRAF | 24173541 | |
| MDA-MB-435 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| HCC2998 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=128 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SK-CO-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-123 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=73 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SNU-C2B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-1034 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-678 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24682747 | |||
| NCI-H747 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-205 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT 116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HuTu-80 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT-15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-411 N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 24682747 | |||
| RKO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3451 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1733 nM | 24784839 | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=142 nM | 24784839 | |||
| MGH-U3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 35612 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38 nM | 24784839 | |||
| KU-19-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36 nM | 24784839 | |||
| LB831-BLC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34 nM | 24784839 | |||
| UM-UC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 647-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24784839 | |||
| J82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 24784839 | |||
| BFTC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SCaBER | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 639-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT112 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9 nM | 24784839 | |||
| T24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SW-1710 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| DSH1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| CAL27 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| Detroit562 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| FUDA | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| SCC25 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| HT-29 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| HCT-116 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| MGC-803 | Function Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 24 h | induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest | 25590805 | |
| MKN-28 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| SGC-7901 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MGC-803 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MV411 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| HL60 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Cliquez pour voir plus de données expérimentales sur la lignée cellulaire | ||||||
Informations chimiques, stockage et stabilité
| Poids moléculaire | 364.4 | Formule | C20H20N4O3 |
Stockage (À compter de la date de réception) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° CAS | 888216-25-9 | Télécharger le SDF | Stockage des solutions mères |
|
|
| Synonymes | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)C1=C(C=C(C(=C1)C2=NNC(=O)N2C3=CC4=C(C=C3)N(C=C4)C)O)O | ||
Solubilité
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(109.76 mM)
Ethanol : 9 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Calculateur de molarité
|
In vivo |
|||||
Calculateur de formulation in vivo (Solution claire)
Étape 1 : Saisir les informations ci-dessous (Recommandé : Un animal supplémentaire pour tenir compte des pertes pendant lexpérience)
Étape 2 : Saisir la formulation in vivo (Ceci est seulement le calculateur, pas la formulation. Veuillez nous contacter dabord sil ny a pas de formulation in vivo dans la section Solubilité.)
Résultats du calcul :
Concentration de travail : mg/ml;
Méthode de préparation du liquide maître DMSO : mg médicament prédissous dans μL DMSO ( Concentration du liquide maître mg/mL, Veuillez nous contacter dabord si la concentration dépasse la solubilité du DMSO du lot de médicament. )
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouterμL PEG300, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouterμL Tween 80, mélanger et clarifier, puis ajouter μL ddH2O, mélanger et clarifier.
Méthode de préparation de la formulation in vivo : Prendre μL DMSO liquide maître, puis ajouter μL Huile de maïs, mélanger et clarifier.
Note : 1. Veuillez vous assurer que le liquide est clair avant dajouter le solvant suivant.
2. Assurez-vous dajouter le(s) solvant(s) dans lordre. Vous devez vous assurer que la solution obtenue, lors de lajout précédent, est une solution claire avant de procéder à lajout du solvant suivant. Des méthodes physiques telles que le vortex, les ultrasons ou le bain-marie chaud peuvent être utilisées pour faciliter la dissolution.
Mécanisme daction
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HSP90
(OSA 8 cells) 4 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Les concentrations inhibitrices à 50 % (IC50) de Ganetespib (STA-9090) contre les lignées de mastocytes malignes sont 10 à 50 fois inférieures à celles du 17-AAG, ce qui indique que la classe de triazolone des inhibiteurs de HSP90 présente probablement une plus grande puissance que les inhibiteurs à base de geldanamycine. Ce composé inhibe les lignées cellulaires MG63 avec une IC50 de 43 nM. Il se lie au domaine de liaison à l'ATP à l'extrémité N de Hsp90 et sert d'inhibiteur puissant de Hsp90 en provoquant la dégradation de plusieurs protéines clientes oncogènes de Hsp90, y compris HER2/neu, EGFR muté, Akt, c-Kit, IGF-1R, PDGFRα, Jak1, Jak2, STAT3, STAT5, HIF-1α, CDC2 et c-Met ainsi que la tumeur de Wilms 1. À de faibles concentrations nanomolaires, il arrête puissamment la prolifération cellulaire et induit l'apoptose dans une grande variété de lignées cellulaires cancéreuses humaines, y compris de nombreuses lignées cellulaires résistantes aux inhibiteurs de tyrosine kinase et à la tanespimycine. Il présente une cytotoxicité puissante dans une gamme de lignées cellulaires tumorales solides et hématologiques, y compris celles qui expriment des kinases mutées qui confèrent une résistance aux inhibiteurs de tyrosine kinase à petites molécules. Son traitement a rapidement entraîné la dégradation des protéines clientes Hsp90 connues, présente une puissance supérieure à l'inhibiteur ansamycine 17-AAG et montre une activité soutenue même avec de courtes durées d'exposition. Dans une autre étude, il induit l'apoptose des lignées cellulaires de mastocytes malins canins. Il est actif à des concentrations significativement plus faibles pour les mastocytes malins canins C2 et BR avec des IC50 de 19 et 4 nM, respectivement, tandis que le 17-AAG inhibe les mastocytes malins canins C2 et BR avec des IC50 de 958 et 44 nM, respectivement. L'expression du Kit WT et muté est régulée à la baisse par 100 nM de ce composé après 24 heures dans toutes les lignées traitées, y compris les cellules C2 et BMCMCs. Cependant, aucun effet sur l'expression de PI3K ou HSP90 n'est observé après traitement.
|
| In vivo |
L'administration de Ganetespib (STA-9090) entraîne une réduction significative de la taille des tumeurs dans plusieurs modèles de xénogreffes tumorales chez la souris et semble moins toxique. De plus, ce composé a démontré une meilleure pénétration tumorale par rapport à la tanespimycine. Il inhibe la croissance tumorale in vivo dans les modèles de xénogreffes de mastocytes malins et d'OSA. Ganetespib inhibe significativement la croissance tumorale lorsqu'il est dosé avec deux cycles répétés de 25 mg/kg/jour pendant 3 jours, avec une valeur %T/C de 18. Il est bien toléré, les groupes véhicule et Ganetespib ayant des changements de poids corporel moyens par rapport au début de l'étude de +0,3 % et -8,1 % au jour 17, respectivement.
|
Références |
|
Applications
| Méthodes | Biomarqueurs | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | EGFR / c-Met / IGF-1Rβ/ Akt / p-Akt / ERK / p-ERK p27(Kip1) / p21 (Cip1) / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin E / Cyclin B1 / CDK1 / CDK2 / CDK4 Survivin / Bcl-2 / Bcl-xl / Mcl-1 B-RAF / C-RAF / N-RAS HER2 / p-STAT3 / BIM CDK1 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin B1 / p27 c-PARP / c-caspase 3 / caspase 8 / c-caspase 8 / caspase 9 / c-caspase 9 ErbB2 / pErbB2 / Src / pSrc / mTOR / pmTOR / Bad / pBad / GSK3 / pGSK3 Wee1 / p-Wee1 / Chk1 / p-Chk1 |
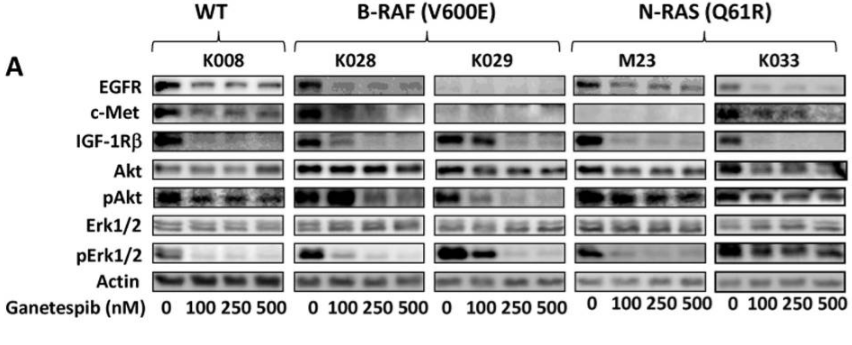
|
23418523 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
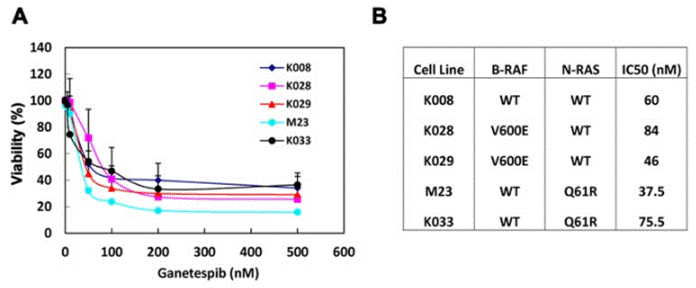
|
23418523 |
Informations sur lessai clinique
(données du https://clinicaltrials.gov, mis à jour le 2024-05-22)
| Numéro NCT | Recrutement | Conditions | Promoteur/Collaborateurs | Date de début | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02192541 | Terminated | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
December 2 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02008877 | Completed | Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST)|Sarcoma |
Sarcoma Alliance for Research through Collaboration|Synta Pharmaceuticals Corp.|United States Department of Defense |
December 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Support technique
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Si vous avez dautres questions, veuillez laisser un message.
Foire aux questions
Question 1:
Does this inhibitor inhibit both isoforms of HSP90?
Réponse :
We don't have the information now and it is not very clear in the literature either. From following two references, it indicates that it might be specific to the alpha form “It binds to the ATP binding site of Hsp90 alpha with a Kd of 110 nM” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3477583/
