Polo-like kinases (PLKs) are a family of evolutionarily conserved Serine/Threonine kinases, which are characterized by the presence of an N-terminal protein kinase domain and a C-terminal Polo-box domain (PBD), playing an important role in the regulation of cell cycle progression through G2 and M (mitosis). [show the full text]
PLK inhibiteurs (PLK Inhibitors)
| N° Cat. | Nom du produit | Information | Citations dutilisation du produit | Validations de produits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2235 | Volasertib (BI6727) | Volasertib est un inhibiteur puissant de Plk1 avec une IC50 de 0,87 nM dans un essai sans cellules. Il montre une sélectivité 6 et 65 fois supérieure contre Plk2 et Plk3. Volasertib induit un arrêt du cycle cellulaire et l'apoptose dans diverses cellules cancéreuses. Phase 3. |
|
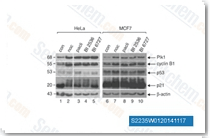
|
| S1109 | BI 2536 | Le BI-2536 est un puissant inhibiteur de Plk1 avec un IC50 de 0,83 nM dans un test sans cellules. Le BI-2536 inhibe la Bromodomain 4 (BRD4) avec un Kd de 37 nM et supprime puissamment l'expression de c-Myc. Le BI-2536 induit l'apoptose et atténue l'autophagie. Phase 2. |
|

|
| S1362 | Rigosertib (ON-01910) | Le Rigosertib (ON-01910) est un inhibiteur non compétitif de l'ATP de PLK1 avec une IC50 de 9 nM dans un essai sans cellule, montrant une sélectivité 30 fois supérieure contre Plk2 et aucune activité sur Plk3. Il inhibe la voie PI3K/Akt, active les signaux de stress oxydatif et induit l'apoptose dans diverses cellules cancéreuses. Ce composé est en phase 3. |
|
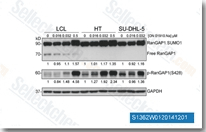
|
| S2193 | GSK461364 | GSK461364 (GSK461364A) inhibe la Plk1 purifiée avec un Ki de 2,2 nM dans un essai sans cellules. Il est plus de 1000 fois sélectif contre Plk2/3. |
|
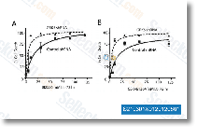
|
| S7255 | Onvansertib (NMS-1286937, NMS-P937) | Onvansertib (NMS-1286937, NMS-P937) est un inhibiteur oralement disponible et sélectif de la Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1) avec une IC50 de 2 nM, et une sélectivité 5000 fois supérieure à PLK2/PLK3. Ce composé provoque puissamment un arrêt du cycle cellulaire mitotique suivi d'une apoptose dans les lignées cellulaires cancéreuses et inhibe la croissance tumorale. Phase 1. |
|
|
| S7552 | CFI-400945 | CFI-400945 est un inhibiteur oralement actif, puissant et sélectif de la polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) avec une valeur Ki de 0,26 nM. |
|
|
| S1485 | HMN-214 | HMN-214 est une prodrogue de HMN-176, qui modifie l'orientation spatiale cellulaire de Plk1. |
|
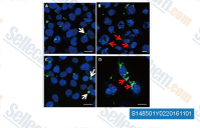
|
| S7248 | Ro3280 | RO3280 (Ro5203280) est un inhibiteur puissant et hautement sélectif de la Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) avec une IC50 de 3 nM. |
|
|
| S7720 | SBE 13 HCl | SBE 13 HCl est un inhibiteur puissant et sélectif de la PLK1 avec une IC50 de 200 pM, et une sélectivité >4000 fois supérieure à celle de l'Aurora A kinase, Plk2 et Plk3. |
|
|
| S2898 | MLN0905 | MLN0905 est un puissant inhibiteur de PLK1 avec une IC50 de 2 nM. |
|
|
PLKs - the Serine/Threonine protein kinases - are structurally comprised of a highly conserved catalytic domain in the N-terminus and a PBD in the C-terminus. The PDB domain is unique for the polo-like kinases family, and essential for their functions such as the subcellular localization and the substrate recognition. Mammalian polo-like kinases (PLK) consists of five members including PLK1 (STPK13), PLK2 (SNK), PLK3 (CNK, FNK or PRK), PLK4 (SAK or STK18), and PLK5. PLKs are critical regulators of cell cycle progression, mitosis, cytokinesis, and the DNA damage response. [1][2]
PLK1 is the most extensively studied member of this family. Through its PBD, PlK1 associates with a large number of proteins, some of which mediate its recruitment to defined cellular structures, such as the centrosomes, kinetochores and the spindle midzone. As reflected by multiple localizations, PLK1 is pivotal in the regulation of diverse cellular and biochemical events at multiple stages of the M phase, including entry into mitosis, centrosome maturation, assembly of the bipolar spindle, sister chromatid splitting, activation of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and exit from mitosis with the initiation of cytokinesis. As PLK1 is essential for cell division, inhibition of PLK1 leads to a failure to complete mitosis, eventually resulting in cell death. PLK2 is classified as an early growth response gene by virtue of its increased expression on stimulation by growth factors. PLK2 is up-regulated by p53 upon irradiation, and the depletion of PLK2 seems to phenocopy the loss of p53 by elevating the sensitivity of cells to spindle poisons. PLK2 is also implicated in centriole duplication, and functions as a regulator of synaptic plasticity in the nervous system. PLK3 is a multifunctional stress response protein. In response to different types of cellular stress, PLK3 activates Chk2 and p53, and plays an important role in genotoxic, hypoxic and oxidative stress responses. Endogenous ectopically expressed PLK3 localizes to the centrosomes during interphase, to the spindle poles during mitosis, and to the midbody during cytokinesis. The overexpression of wild-type or mutant forms of PLK3 induces G2/M arrest and eventually apoptosis. PlK4 is crucial for the duplication of the centrioles, and essential for early embryogenesis. The overexpression of PLK4 induces multinucleated cells that are associated with a progressive loss of cell viability. Although PLK5 has a truncated kinase domain that lacks kinase activity of catalytic activity, PLK5 retains important functions in neuron biology. Overexpression of PLK5 induces G1 cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis. PLK5 can be induced by various stress-promoting agents, which is independent of p53 in contrast to PLK2 and PLK3. [1][2][3]
Polo-like kinases are dysregulated in a variety of human cancers. Consistent with the critical functions of PLK1 during M-phase progression, PLK1 is highly expressed in tumors including those derived from lung, breast, colon, pancreas, prostate and ovary. Over-expression of PLK1 correlates with cellular proliferation and poor prognosis, and PLK1 depletion is associated with a decrease in cell viability and induction of apoptosis in various cancerous cells, indicating that PLK1 is a promising target in oncology. Small-molecule inhibitors of PLK1 have become attractive candidates for anticancer drug development targeting the kinase domain and the PBD of PLK1, and a variety of PLK1 inhibitors (GW843682X, BI 2536, et al.) have been clinically assessed and hold great promise for the improved treatment of cancer patients. [1][2]
